Generate Ssh Host Key Windows
A host key is a cryptographic key used for authenticating computers in the SSH protocol. Host keys are key pairs, typically using the RSA, DSA, or ECDSA algorithms. Public host keys are stored on and/or distributed to SSH clients, and private keys are stored on SSH servers. Set up your first SSH keys. Use SSH keys for authentication when you are connecting to your server, or even between your servers. They can greatly simplify and increase the security of your login process. When keys are implemented correctly they provide a secure, fast, and easy way of accessing your cloud server. Apr 19, 2019 How to generate SSH keys in OpenSSH for Windows 10 Install the OpenSSH module for PowerShell. Generate user key pair. In PowerShell, change directories to the path above where. Copying the public key securely. The OpenSSH tools include the SCP and SFTP utilities.
Set up your first SSH keys
The ided25519.pub file is your public key. Then run ssh-keygen and follow the prompt to generate your private key files and move the authorizedkeys in.ssh on your host. Finally open Services Manager window, and click Start with sshd service. The password authentication method works well. Aug 19, 2019 Using SSH keys for authentication is highly recommended, as a safer alternative to passwords. This tutorial will guide you through the steps on how to generate and set up SSH keys on CentOS 7. We also cover connecting to a remote server using the keys. May 05, 2019 Creating SSH keys with PuTTYgen # To generate an SSH key pair on Windows using PuTTYgen perform the following steps: Start the PuTTYgen tool, by double-clicking on its.exe file or going to the Windows Start menu → PuTTY (64-bit) → PuTTYgen. For “Type of.
Use SSH keys for authentication when you are connecting to your server, or even between your servers. They can greatly simplify and increase the security of your login process. When keys are implemented correctly they provide a secure, fast, and easy way of accessing your cloud server.
Follow our guide and learn how to set up your first SSH keys for authentication using OpenSSH or PuTTYTray.
Preparing your server
To add an SSH key pair, first, create a hidden folder to your user account home directory on your cloud server with the following command.
Then restrict the permissions to that directory to just yourself with the command below.
This creates a secure location for you to save your SSH keys for authentication. However, note that since the keys are stored in your user home directory, every user that wishes to connect using SSH keys for authentication has to repeat these steps on their own profile.
Using OpenSSH to generate a key pair
Now continue on your own computer if you are using Linux or any other OS that has OpenSSH. PuTTY users should skip to the next section.
1. Generate a new key pair in a terminal with the next command
The key generator will ask for location and file name to which the key is saved to. Enter a new name or use the default by pressing enter.
2. (Optional) Create a passphrase for the key when prompted
This is a simple password that will protect your private key should someone be able to get their hands on it. Enter the password you wish or continue without a password. Press enter twice. Note that some automation tools might not be able to unlock passphrase-protected private keys.
3. Copy the public half of the key pair to your cloud server using the following command
Replace the user and server with your username and the server address you wish to use the key authentication on.
This also assumes you saved the key pair using the default file name and location. If not, just replace the key path ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub above with your own key name.
Enter your user account password for that SSH server when prompted.
You can now authenticate to your server with the key pair, but at the moment you would need to enter the passphrase every time you connect.
4. (Optional) Set up SSH Agent to store the keys to avoid having to re-enter passphrase at every login
Enter the following commands to start the agent and add the private SSH key.
Type in your key’s current passphrase when asked. If you saved the private key somewhere other than the default location and name, you’ll have to specify it when adding the key.
Afterwards, you can connect to your cloud server using the keys for authentication, and only having to unlock the key by repeating the last 2 steps once after every computer restart.
Using PuTTYTray to generate a key pair
If you are running Windows and PuTTYTray for SSH, you can use the built-in key generator from PuTTY to create a new key pair.
1. Click the Keygen button at the bottom of the PuTTY Configuration window to get started.
Then in the Key Generator window, check that the Type of key to generate at the bottom is set to SSH-2 RSA. The older SSH-1 was the first version on the standard but is now generally considered obsolete. Most modern servers and clients support SSH-2.
2. Click the Generate button to begin.
3. Keep moving your mouse over the blank area in any manner to help generate randomness for a few moments until the progress is complete.
With the keys finished, PuTTY will show the relative information about the pair along with the public key for easier copying.
4. (Optional) Enter a key passphrase in the 2 empty fields for the added security before continuing. The passphrase will protect your key from unauthorized use should someone be able to copy it. However, some automation tools might not be able to unlock passphrase-protected private keys.
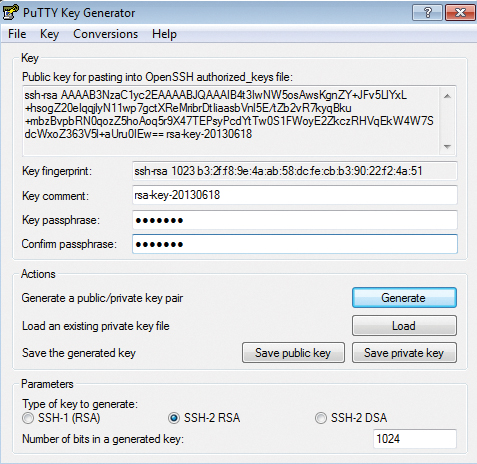
5. Click the Save private key button and store it somewhere safe. Generally anywhere in your user directory is fine as long as your PC is password protected. Before closing the keygen, you may want to copy the public key to your clipboard, but you can always get it later as well.
Now that you have a new key saved on your computer, you’ll need to import it into the PuTTY key agent.
6. Click the Agent button to open the key manager in the PuTTY Configuration window.
7. Click Add Key button in the Key List, then browse to the location you saved the private key, select it and click Open.
Enter your key passphrase if asked.
This will import the key to your PuTTY client, but you still need to copy the public key over to your server.
8. Open an SSH connection to your cloud server and go to the SSH key directory.
9. Open or create the default file OpenSSH looks for public keys called authorized_keys.
Generate Ssh Host Key Windows 7
10. Paste the public key into the file by simply right-clicking the SSH client window. Make sure the key goes on a single line for OpenSSH to be able to read it.
When you’ve copied the public key over to the authorized keys list, save the file and exit the editor. You can now test the public key authentication by logging in to your server again. You should not get asked for your password, but instead logged straight in with the key. If it’s not working, check that your private key is unlocked at your SSH Agent and try again.
Turn off password authentication
With SSH key authentication configured and tested, you can disable password authentication for SSH all together to prevent brute-forcing. When logged in to your cloud server.
1. Open the SSH configuration file with the following command.
2. Set the password authentication to no to disable clear text passwords.
3. Check that public key authentication is enabled, just to be safe and not get locked out from your server. If you do find yourself unable to log in with SSH, you can always use the Web terminal at your UpCloud control panel.
Then save and exit the editor.
4. Restart the SSH service to apply the changes by using the command below.
With that done your cloud server is now another step along towards security. Malicious attempts to connect to your server will results in authentication rejection, as plain passwords are not allowed, and brute-forcing an RSA key is practically impossible.
Conclusions
Remember to always keep your private keys safe. You can use the same key from multiple computers if you wish, or generate new ones on each client connecting to your cloud server for added security. Each user should generate their own key pair and passphrase for secure access control. With proper management, even in case one of the private keys gets compromised you won’t have to replace them all.
The secure shell (ssh) protocol is used for remote system access, remote file transfer in Unix. Now the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update comes with the native OpenSSH feature, which have both client and server for installation on your tablet or computer. An OpenSSH implementation is the value of the OS increases, and here are the how-to tips to enable and setup OpenSSH Server.
The Openssh folder is located in c:windowssystem32 of File Explorer. The server uses the port 22, so ensure the firewall allows the traffic on port 22. The Openssh feature is still at a BETA stage, and have some stability issues.
How to Enable OpenSSH Server and setup OpenSSH in Windows 10
* Make sure your account is an Administrator.
* Tap or click on the Windows button at left-bottom corner of your desktop.
* Open the Settings app from Start menu.
* Click on Apps category, and select the Apps & features tab.
* Go to its right side pane, click Manage optional features link.
* Click the “Add a feature” button.
* Locate the “OpenSSH Server” item and select it, then click Install button to get it.
* Once the OpenSSH software has been applied, restart Windows 10 to take effects.
For Password-based authentication
* Press Win + R from your keyboard, type services.msc and press Enter to open the Services Manager.
* Double-click the sshd entry, go to the “Log On” tab, it lists which user account used by sshd server. If this account doesn’t have password, go to set up a password.
Generate ssh key mac. If you use public key authenticationIf you do use keys to authenticate, you should regenerate them. Start by backing up your old key. SSH regulars will be familiar with most of the commands used. This disables the roaming feature, which was part of the problem: UseRoaming noGenerate new keys-$ ssh-keygenGenerating public/private rsa key pair.Enter file in which to save the key (/home/example/.ssh/idrsa):Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):Enter same passphrase again:Your identification has been saved in /home/example/.ssh/idrsa.Your public key has been saved in /home/example/.ssh/idrsa.pub.Now copy the new public key over, using the old keys. Assuming it’s at the default location, just use- $ mv /.ssh/idrsa /.ssh/idrsa.old$ mv /.ssh/idrsa.pub /.ssh/idrsa.pub.oldNext, create or edit /.ssh/config, and add the following line.
For Key-based authentication
* Open an elevated command prompt, type the command below and press Enter to navigate to Openssh directory:
cd c:windowssystem32Openssh
Generate Ssh Host Key Windows 6
* Execute another command to generate security keys for the sshd server:
Warcraft 3 frozen throne cd key generator. ssh-keygen -A

It will result ssh-keygen: generating new host keys: ed25519. The id_ed25519.pub file is your public key.
* Then run ssh-keygen and follow the prompt to generate your private key files and move the authorized_keys in ~.ssh on your host.
* Finally open Services Manager window, and click Start with sshd service.
The password authentication method works well. However, I can’t make SSH run in Windows 10, because it doesn’t accept my RSA key. I notice that only ed25519 keys are supported at present. So I go to use the PuTTY tool.